Table Of Contents
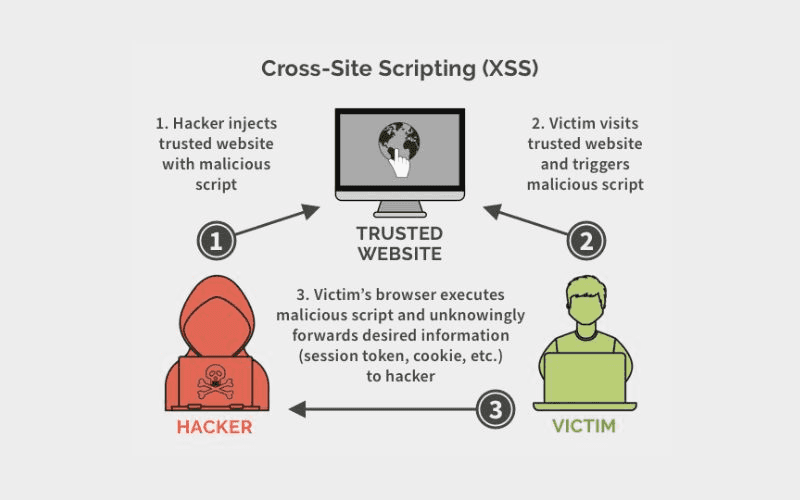
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is a security vulnerability that allows attackers to inject and execute malicious code (usually JavaScript) in a legitimate website that users visit.
Because the browser treats this injected code as trusted content, attackers can:
- Steal cookies and session tokens
- Impersonate users
- Take over accounts
Unlike server-side attacks, XSS happens entirely in the user’s browser, making it harder to detect and block.
How XSS Works
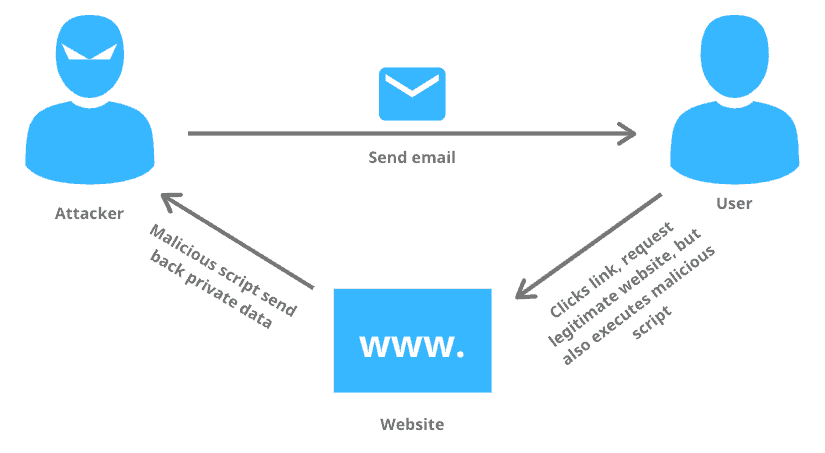
- Attacker finds an input point (form, URL, comment, search field)
- Injects malicious JavaScript
- User visits the affected page
- Browser executes the script
- Attacker steals data or controls the session
Root cause:
- No input validation
- No output encoding
Attackers use XSS to:
- Steal cookies, tokens, and personal data
- Spread malware
Common Types
1. Stored XSS (Persistent XSS)
The most dangerous type. Malicious code is stored permanently on the server.
How it works:
- Attacker submits a comment containing malicious code
- Server stores it in the database
- Every user who views the page runs the malicious script
2. Reflected XSS (Non-persistent XSS)
The most common type. The malicious code is embedded in a URL and reflected back to the user.
How it works:
- Attacker crafts a malicious link
- Victim clicks it
- The injected script runs in the browser
Prevent
- Validate and filter all user input
- Use HttpOnly & Secure cookies
- Keep dependencies updated
- Train development teams
