Table Of Contents
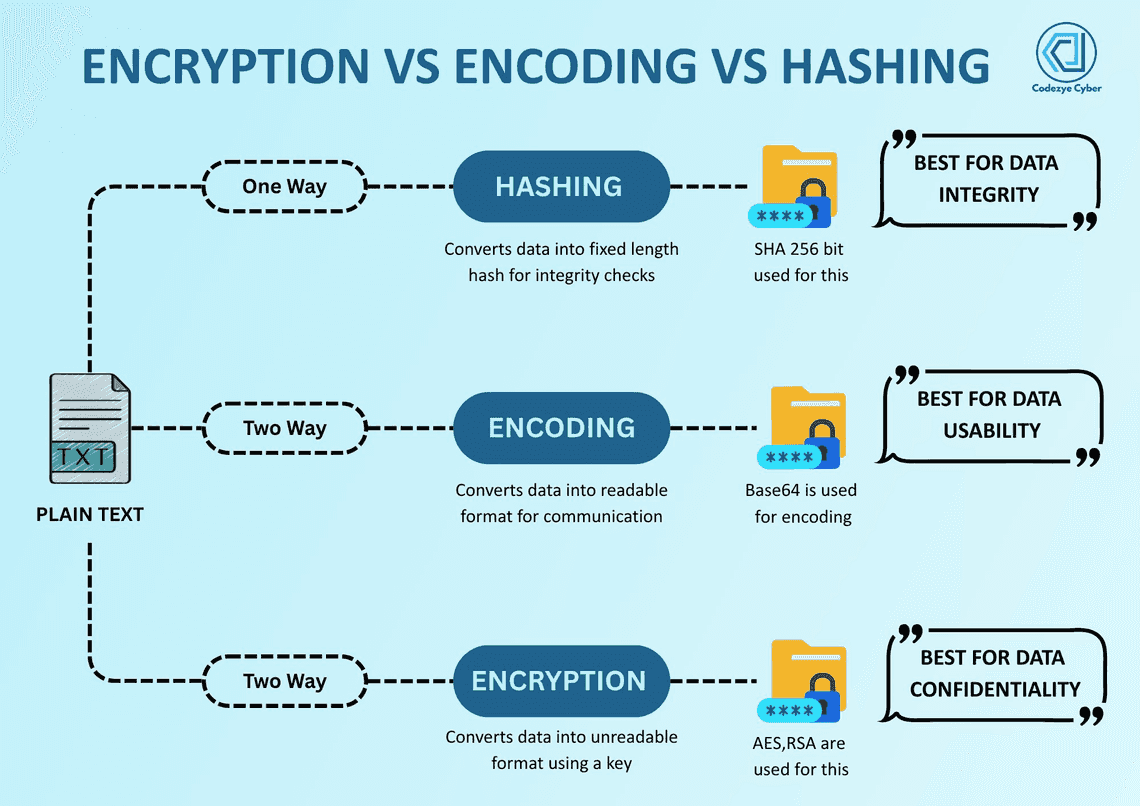
Hashing vs Encoding vs Encryption
| Concept | Real Example | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Hashing | Password login | Verify without revealing |
| Encoding | Email attachment | Compatibility |
| Encryption | HTTPS banking | Confidentiality |
How to store passwords in Database securely?
- Hashing is a one-way function that converts input data (like a password) into a fixed-size string of characters, which appears random. It is designed to be irreversible, meaning you cannot retrieve the original input from the hash.
- Encoding is a reversible process that transforms data into a different format using a scheme that is publicly available. It is primarily used for data integrity and compatibility, not security.
- Encryption is a two-way function that transforms data into a secure format using an algorithm and a key.
TLS/SSL Handshake
SSL/TLS = Encryption + Authentication + Integrity for internet communication
When a browser connects to an HTTPS website, it performs a TLS handshake to create a secure connection.
First, the browser and server agree on the TLS version and encryption algorithms.
The server then sends its SSL/TLS certificate, which contains its public key and is signed by a trusted Certificate Authority.
The browser verifies this certificate using built-in CA public keys to make sure the server is legitimate.
After that, the browser and server securely exchange key material and independently generate the same session key.
Once the handshake finishes, all further communication is encrypted using fast symmetric encryption like AES.
This ensures confidentiality, authentication, and data integrity for HTTPS traffic.
What happens when you type google.com and hit enter on browser?
CORS
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a browser security mechanism that controls whether a web page can access resources from another origin (different domain, protocol, or port).
It exists to relax the Same-Origin Policy safely.
Browser sends request with:
Origin: https://frontend.comServer responds with headers like:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://frontend.comBrowser checks the headers
- If allowed → response is accessible
- If not → browser blocks it
⚠️ CORS is enforced by the browser, not the server.
Why does CORS exist?
CORS is a browser security mechanism that controls cross-origin HTTP requests.
When a web app makes a request to a different origin, the browser adds an Origin header and checks the server’s CORS response headers.
If the server allows the origin, the browser lets the response through; otherwise, it blocks it.
For complex requests, the browser sends a preflight OPTIONS request first.
CORS protects users while still allowing safe cross-domain communication.
