Table Of Contents
JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained way to securely transmit information between parties as a JSON object.
JWTs are commonly used for authentication and authorization in modern web applications.
JWT is widely adopted in APIs, SPAs, and microservice architectures because it is:
- Stateless – no server-side session storage required
- Compact – small size, efficient to send via HTTP headers
- Self-contained – carries user identity and metadata
- Scalable – works well with distributed systems
Structure
A JWT consists of three parts, separated by dots (.):
header.payload.signature
Each part is Base64URL-encoded.
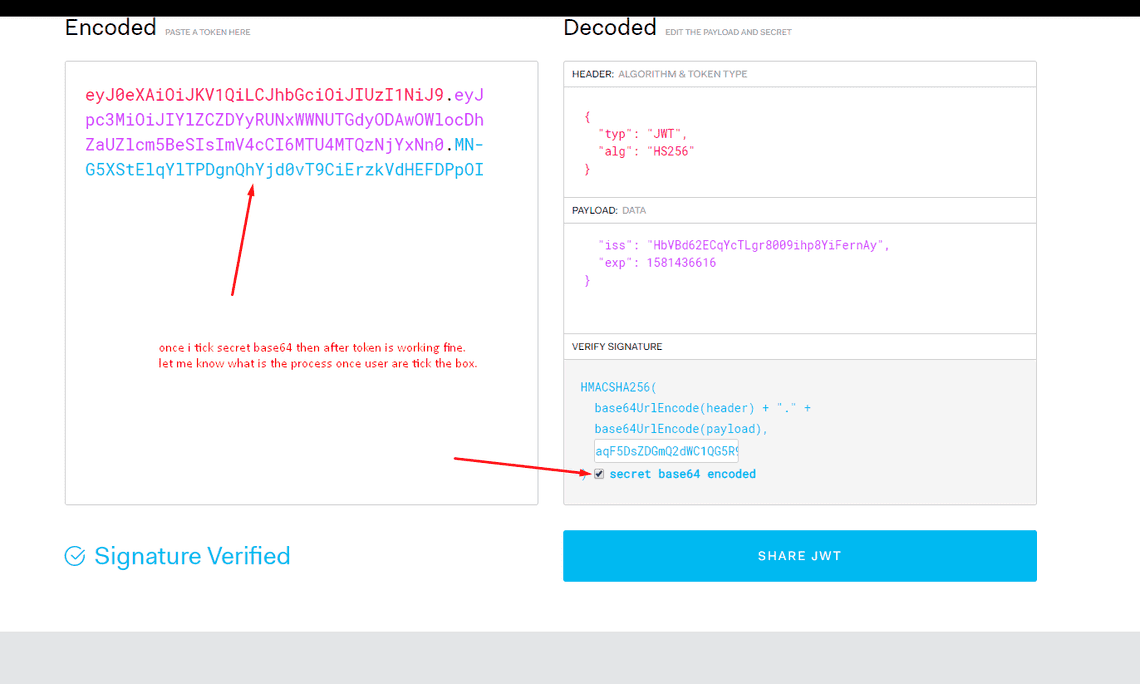
1. Header
The header describes the token type and the signing algorithm.
{"alg": "HS256","typ": "JWT"}
alg: signing algorithm (HS256, RS256, etc.)typ: token type (JWT)
2. Payload
The payload contains claims, which are statements about the user and additional metadata.
There are three types of claims:
Registered claims (standard):
iss(issuer)sub(subject / user id)exp(expiration time)aud(audience)
Public claims Custom but globally agreed-upon fields.
Private claims Custom fields shared between specific systems (e.g.
role,email).
⚠️ Important: The payload is not encrypted, only encoded.
3. Signature
The signature ensures the token has not been altered.
Example (HS256):
HMACSHA256(base64UrlEncode(header) + "." +base64UrlEncode(payload),secret)
The server verifies the signature to confirm the token is valid and trustworthy.
How Its Work
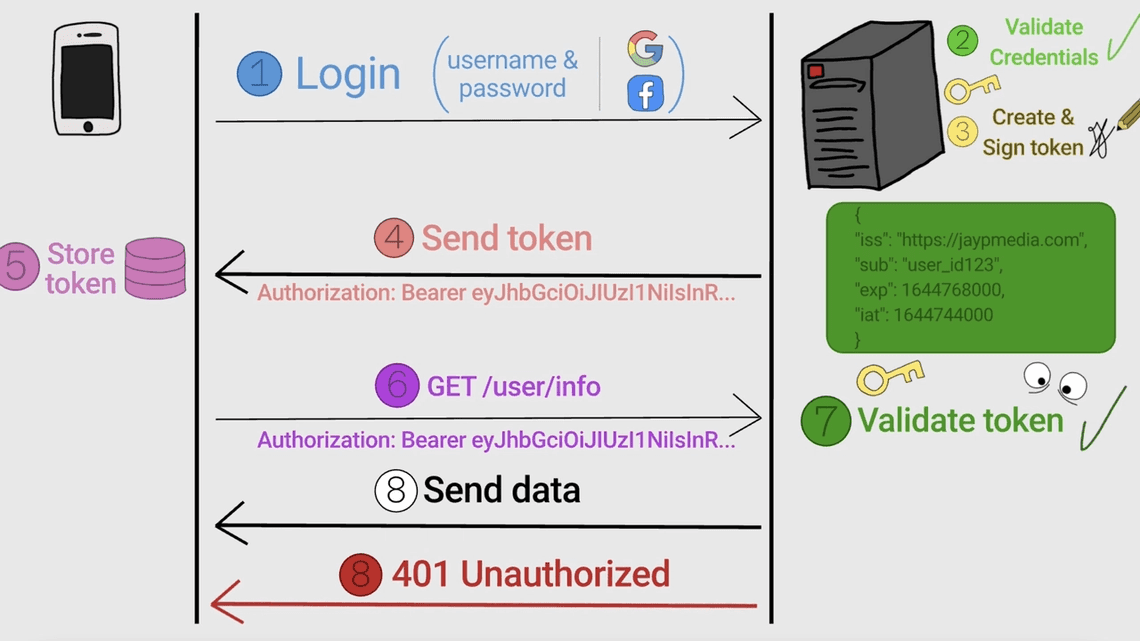
User logs in with credentials
Server validates credentials and generates a JWT
Client stores the token (cookie or memory)
Client sends JWT in every request:
Authorization: Bearer <token>Server verifies the token and grants access
