Table Of Contents
Understanding how React updates the UI starts with understanding the difference between the DOM and the Virtual DOM. These concepts explain why React apps are fast, scalable, and efficient.
DOM
The DOM (Document Object Model) is a tree-like structure created by the browser that represents the HTML on your page.
- Every element becomes a node
- Updating the DOM directly is slow
- Even small changes can trigger costly reflows and repaints
Example:
<div><h1>Hello</h1></div>
The browser converts this into a live object structure it can render.
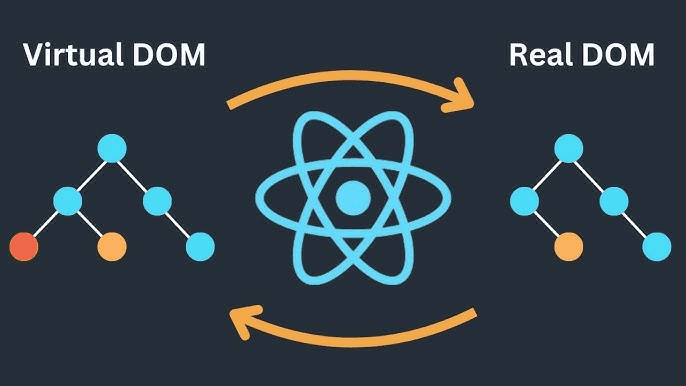
Virtual DOM
The Virtual DOM is a lightweight JavaScript representation of the real DOM used by React.
- It exists in memory
- It’s fast to create and compare
- It allows React to compute changes efficiently before touching the real DOM
Think of it as a blueprint React uses to plan updates.
How React Uses the Virtual DOM
When state changes in React:
- React creates a new Virtual DOM tree
- Compares it with the previous one (diffing)
- Figures out the minimal set of changes
- Updates only what’s needed in the real DOM
This process is called reconciliation.
Why Virtual DOM Improves Performance
Instead of rewriting the whole DOM, React:
✔ Updates only changed nodes.
✔ Reduces direct DOM operations.
✔ Batches updates efficiently.
✔ Improves UI consistency.
Important Clarification
The Virtual DOM itself isn’t faster than the DOM — What makes React fast is how it minimizes DOM operations by using the Virtual DOM intelligently.
