C# DECISION MAKING

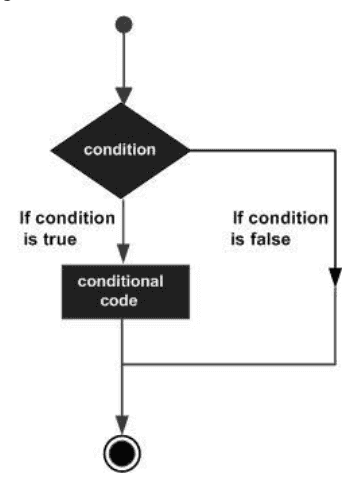
Decision making structures requires the programmer to specify one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements to be executed if the condition is determined to be true, and optionally, other statements to be executed if the condition is determined to be false.
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| if statement | An if statement consists of a boolean expression followed by one or more statements. |
| if…else statement | An if statement can be followed by an optional else statement, which executes when the boolean expression is false. |
| nested if statements | You can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement(s). |
| switch statement | A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values |
| nested switch statements | You can use one switch statement inside another switchstatement(s). |
The if…else if…else Statement
An if statement can be followed by an optional else if…else statement, which is very useful to test various conditions using single if…else if statement.
It is always legal in C# to nest if-else statements, which means you can use one if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement(s)
using System;namespace ConsoleApp1{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){/* local variable definition */int a = 100;/* check the boolean condition */if (a == 10){/* if condition is true then print the following */Console.WriteLine("Value of a is 10");}else if (a == 20){/* if else if condition is true */Console.WriteLine("Value of a is 20");}else if (a == 30){/* if else if condition is true */Console.WriteLine("Value of a is 30");}else{/* if none of the conditions is true */Console.WriteLine("None of the values is matching");}Console.WriteLine("Exact value of a is: {0}", a);Console.ReadLine();//None of the values is matching//Exact value of a is: 100}}}
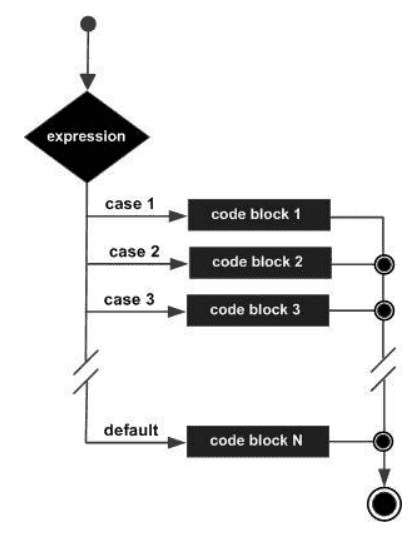
Switch Statement
A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. Each value is called a case, and the variable being switched on is checked for each switch case.
using System;namespace ConsoleApp1{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){/* local variable definition */char grade = 'B';switch (grade){case 'A':Console.WriteLine("Excellent!");break;case 'B':case 'C':Console.WriteLine("Well done");break;case 'D':Console.WriteLine("You passed");break;case 'F':Console.WriteLine("Better try again");break;default:Console.WriteLine("Invalid grade");break;}Console.WriteLine("Your grade is {0}", grade);Console.ReadLine();//Well done//Your grade is B}}}
The ? : Operator
We have covered conditional operator ? : in previous chapter which can be used to replace if…else statements. It has the following general form:
Exp1 ? Exp2 : Exp3;
Tags
Share
Table Of Contents
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff
Social Media
